In the field of automotive design and manufacturing, the optical solution of car lights is of vital importance. It not only concerns the aesthetic appearance of the vehicle but also directly affects the functionality of driving.
Today, we focus on studying the optical schemes of signal lights. Different optical schemes have a significant impact on the cost and optical effect of vehicle lights. The design of the optical scheme for signal lights is also a major difficulty in the overall design and development of the lights.

I. LED+ Light Guide Strip Scheme
(1) LED+ Light Guide + Inner Mask (Built-in)
(2) LED+ Light Guide + Thick and Thin Wall Component
Principle:
The light emitted by the LED light source is conducted through the light guide strip, and the inner mask or thick and thin wall component further processes the light. In the inner mask type, the light starts from the LED, is transmitted through the light guide strip, and the final light distribution is achieved by the inner mask. The thin and thick wall type utilizes the structural characteristics of the wall to create a light effect, making the appearance more textured and forming the texture effect of a conventional thick wall, but there is a limit to the height of the protruding shape.
Function Application:
Mainly used for various signal lights, such as position lights, daytime running lights and turn signals. With its light transmission and processing mechanism, it can provide clear and recognizable light signals in different driving scenarios.

Advantages:
In terms of static appearance, the inner mask type has good uniformity in lighting, allowing for the integration of yellow and white light, resulting in a relatively soft and unified visual effect. The light uniformity of the thin and thick wall type is medium, similar to the appearance effect of the thick wall type, and can also achieve the integration of yellow and white light. This solution can create a simple and highly recognizable lighting effect for the vehicle, allowing other road users to clearly identify the vehicle’s status during daily driving.
• Disadvantages
• Both types have the problem of bright spots at the end of the light guide. The end shielding area will affect the shape structure and cannot achieve the effect of flowing light, which is limited in the dynamic expression of the light. The bright spots at the end of the light guide may affect the overall aesthetic appeal of the lighting, and the inability to light up in a continuous stream makes the vehicle lack the interest and technological sense of the lighting display, especially in some scenarios that pursue personalized lighting effects, it is difficult to meet the demands.

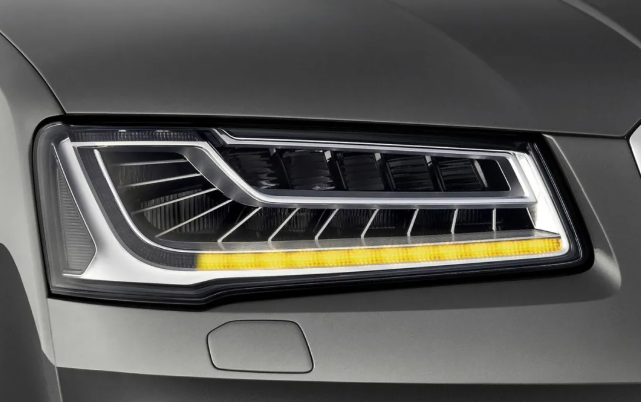
1. Side-projection LED+ Mirror Scheme
(1) LED+ Mirror + Internal Configuration
(2) LED+ Mirror + Thin and Thick Wall Components
(3) LED+ Mirror + Discrete Internal Configuration
• Principle
• The light from the LED light source is reflected and distributed by means of the mirror. Built-in mirrors, thin and thick wall pieces or discrete built-in components play an auxiliary role in light processing and appearance shaping. In the endoscope scheme, after the reflector reflects the light, the endoscope further adjusts the shape of the light. The thin and thick wall component scheme utilizes the wall component structure and the reflector to coordinate and control the light. The discrete internal distribution scheme achieves light distribution through the combination of special internal distribution materials and mirrors.

Function application:
Widely used in position lights, daytime running lights and turn signals. It can provide appropriate lighting and signal indication for the vehicle in different driving states.

Advantages:
The interior mirror solution has a medium uniformity of lighting. The interior mirror is a large flat surface without patterns, which can achieve a flowing effect, adding dynamic lighting beauty to the vehicle and enhancing its recognition and technological feel. The thin-walled and thick-walled part scheme is similar to the appearance effect of thick-walled parts. Both sides of the thick-walled parts can have light-distributing patterns. The uniformity of the light is average but can be illuminated in a flowing manner. This scheme ensures a certain degree of light uniformity while increasing the visual richness of the light through flowing lighting and light-distributing patterns. The discrete internal configuration scheme can only achieve the position light function. The internal configuration is a large plane without patterns, with good light uniformity and can be illuminated in a flowing manner. Its excellent uniformity makes the display effect of the position light clear and stable.
Disadvantages:
The interior mirror scheme has average transparency in appearance, with patterns faintly visible, which may affect the purity of the light and the overall visual effect to a certain extent. Dark areas are prone to occur at the partition points of the thin and thick wall component schemes, which will lead to imperfect light distribution and affect the overall quality of the lighting. The discrete internal distribution scheme has an opaque appearance, low white luminous efficacy, can only be used as a position light and has dark areas with wall thickness. Its function is relatively single, and it has deficiencies in both luminous efficacy and appearance.

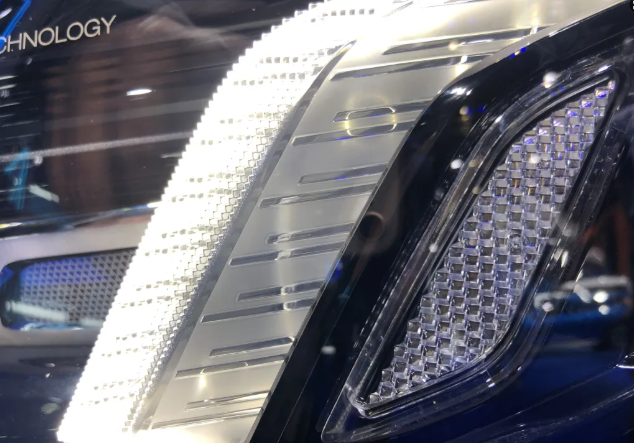
3. LED Side Projection Scheme (Thick-walled Component)
• Principle:
The LED light source projects light from the side. By using the structure of the thick-walled component, the light is conducted, reflected and diffused, thereby achieving a specific light distribution.

Functional application:
It is used for position lights, daytime running lights and turn signals, providing necessary light signals for vehicles in various driving scenarios.

Advantages:
The static appearance has a transparent and crystal clear effect, can achieve a flowing water effect, and is visually more beautiful. This unique appearance effect can make the vehicle stand out among numerous models, enhance the vehicle’s appearance level and uniqueness, and meet consumers’ pursuit of personalized vehicle appearance.
Disadvantages:
Its light direction depth is related to uniformity, and it has a large demand for rear space. When the vehicle’s space layout is limited, there may be installation adaptation issues. If the rear space of the vehicle is compact, adopting this solution may encounter installation difficulties and even affect the layout of other components, limiting its application in some models. At the same time, the cost is also higher than other solutions.
5. Principle of LED Direct Projection Scheme (Thick-walled Components)
The LED light source directly projects light onto the thick-walled components. Relying on the optical properties of the thick-walled components themselves, such as refraction and scattering, the light is processed and diffused to achieve the expected light distribution effect. In this scheme, the light starts from the LED chip and acts directly on the thick-walled component without the complex intermediate conduction structure.
The functional application can be applied to basic lighting and signal functional scenarios such as position lights, daytime running lights, and turn signals. Due to its characteristic of direct light projection, it can play a role in some situations where the direct output response of light is highly demanded, such as performing well in scenarios where rapid lighting is needed to indicate the vehicle status.

The advantage is that the structure is relatively simple.
Compared with some complex optical solutions, the LED direct projection solution makes the layout of the PCB simpler and reduces the complexity of the overall structure to a certain extent. The assembly is simple, and the space is only required in the X direction.
Disadvantages:
Stringent requirements for the shape: In terms of shape design, this scheme has strict restrictions on the height difference of the luminous shape. If the difference in the light-emitting shape is too large, the conventional printed circuit board (PCB) will not be able to meet the requirements, and a flexible circuit board (FPC) needs to be used instead. However, the cost of FPC is relatively high, which will significantly increase the manufacturing cost of the entire vehicle lighting system and is extremely unfavorable for cost control.
• Great challenge to uniformity: The LED direct projection solution is prone to causing LED bright spots, which poses a significant test to the uniformity of the light. Uneven lighting can cause some areas to be too bright while others are too dark, affecting the visual effect of the lighting. This unevenness may lead to the scheme failing to meet the design standards.
5. Scheme Comparison and Selection Suggestions
Different optical schemes for vehicle lamps each have their own advantages and disadvantages. From the perspective of light uniformity, the inner mask type of LED + light guide strip and the discrete internal matching type of LED + mirror perform better. In terms of achieving the flowing lighting effect, the internal mirror configuration of LED + mirror, the types of thin and thick wall components, and the LED side projection solution have more advantages. In terms of appearance, the LED side-projection solution stands out for its transparent and crystal clear appearance, but it has a disadvantage in terms of cost. Although the LED direct projection solution (thick-walled components) has a simple structure and assembly and a fast response, it has certain requirements in terms of shape.

In practical applications, car manufacturers need to comprehensively consider multiple aspects such as cost, whether there is a flowing light flow, and whether the texture of the appearance is required. Weigh the cost input and production process difficulty of each plan to achieve the best cost performance and product performance.

In conclusion, the selection of an optical solution for vehicle lamps is a comprehensive decision-making process that requires a balance to be struck among technical characteristics, functional requirements, and practical applications, so as to create an automotive lighting system that is both aesthetically pleasing and practical.